
Lake Formation とは
AWS の提供するデータレイク構築のためのマネージドサービスです。
- Glue のクローラを利用して各データソースからデータカタログを生成
- Lake Formation の提供するブループリントにより、データレイク構築のための Glue ワークフローを生成
- データレイクは Glue ワークフローに含まれる Job により S3 上に構築
- データレイクへの柔軟なアクセスパーミッションが可能となる
Lake Formation を利用する主要な利点は、アクセスパーミッションの柔軟な管理が可能になる点にあります。 テーブル単位であったりカラム単位などの細かい粒度でのデータアクセス制御が可能となります。
ブループリント
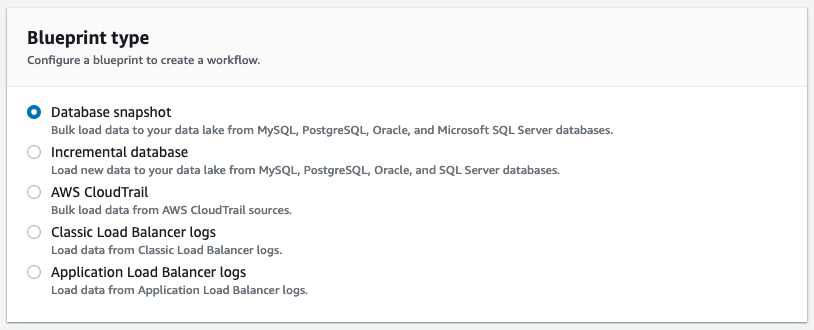
現時点では Lake Formation が提供するブループリントは大きくデータベース用とログファイル用のものが用意されており、以下の5種があります。
- データベーススナップショット
- 増分データベース
- AWS CloudTrail
- Classic Load Balancer ログ
- Application Load Balancer ログ
増分データベース は、追加型のデータについてデータレイクへの差分反映を行うものです。
データベーススナップショット用のブループリントを例に、作成される Glue ワークフローがどのようなものかを見てみましょう。
Glue ワークフロー
Lake Formation でブループリントからワークフローを作成すると、以下のような Glue ワークフローが作成されます。

なにやら大量のジョブが生成されますが、内容としてはたいしたものではありません。
以下の流れのワークフローとなります。
- 開始トリガ
- Glue クローラ事前ジョブ
- Glue クローラ
- Glue クローラ事後ジョブ
- ETL トリガ
- ETL ジョブ
- ETL 事後トリガ
- ETL 事後ジョブ
ETL ジョブは、Apache Spark による分散処理が行われます。 ブループリントで並列数を指定でき、デフォルトは5並列で、15並列まで設定可能です。
トリガとクローラは、単にGlue のトリガとクローラ であり、ジョブは Python コードとして生成されます。
それぞれのジョブの内容について見てみましょう。
Glue クローラ事前ジョブ
クロール前のジョブです。
import utils FAILURE_STATE_TRANSITION_MAP = { 'DISCOVERING': 'DISCOVERY FAILED', 'IMPORTING': 'IMPORT FAILED', 'DISCOVERY FAILED': 'DISCOVERY FAILED', 'IMPORT FAILED': 'IMPORT FAILED' } def main(): args = utils.get_job_args([ 'WORKFLOW_NAME', 'WORKFLOW_RUN_ID', 'transition_state', 'glue_endpoint', 'region' ], []) workflow_name = args['WORKFLOW_NAME'] workflow_run_id = args['WORKFLOW_RUN_ID'] transition_state = args['transition_state'] glue_endpoint = args['glue_endpoint'] region = args['region'] client = utils.build_glue_client(region, glue_endpoint, True) state_to_set = transition_state run_properties = client.get_workflow_run_properties(Name=workflow_name, RunId=workflow_run_id)["RunProperties"] if transition_state == 'FAILED' and \ 'run_state' in run_properties and \ run_properties['run_state'] in FAILURE_STATE_TRANSITION_MAP: state_to_set = FAILURE_STATE_TRANSITION_MAP[run_properties['run_state']] if 'run_state' in run_properties: print("[INFO]: WORKFLOW {} CHANGING FROM STATE {} -> {}".format(workflow_name, run_properties['run_state'], transition_state)) run_properties['run_state'] = state_to_set client.put_workflow_run_properties(Name=workflow_name, RunId=workflow_run_id, RunProperties=run_properties) main()
なにやら長いですが、やっていることは、次の遷移状態に切り替えているだけです。
Glue API により get_workflow_run_properties() でワークフロー実行プロパティを取得し、実行状態を遷移先の状態として put_workflow_run_properties() に書き出しています。
状態は DISCOVERING となります。
このジョブの後でクロールが実行されます。 クロールでは、指定されたデータソースからGlueのデータカタログを構成します。
Glue クローラ事後ジョブ
このジョブは Glue のクロール処理の後に呼び出されます。
やっていることは、前述と同じで、状態の更新のみです。
import utils FAILURE_STATE_TRANSITION_MAP = { 'DISCOVERING': 'DISCOVERY FAILED', 'IMPORTING': 'IMPORT FAILED', 'DISCOVERY FAILED': 'DISCOVERY FAILED', 'IMPORT FAILED': 'IMPORT FAILED' } def main(): args = utils.get_job_args([ 'WORKFLOW_NAME', 'WORKFLOW_RUN_ID', 'transition_state', 'glue_endpoint', 'region' ], []) workflow_name = args['WORKFLOW_NAME'] workflow_run_id = args['WORKFLOW_RUN_ID'] transition_state = args['transition_state'] glue_endpoint = args['glue_endpoint'] region = args['region'] client = utils.build_glue_client(region, glue_endpoint, True) state_to_set = transition_state run_properties = client.get_workflow_run_properties(Name=workflow_name, RunId=workflow_run_id)["RunProperties"] if transition_state == 'FAILED' and \ 'run_state' in run_properties and \ run_properties['run_state'] in FAILURE_STATE_TRANSITION_MAP: state_to_set = FAILURE_STATE_TRANSITION_MAP[run_properties['run_state']] if 'run_state' in run_properties: print("[INFO]: WORKFLOW {} CHANGING FROM STATE {} -> {}".format(workflow_name, run_properties['run_state'], transition_state)) run_properties['run_state'] = state_to_set client.put_workflow_run_properties(Name=workflow_name, RunId=workflow_run_id, RunProperties=run_properties) main()
このジョブによりワークフローの状態は IMPORTING となります。
ETL ジョブ
ここがワークフローの本丸の ELT 処理になります。
# Copyright 2018-2019 Amazon.com, Inc. or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. # Licensed under the Amazon Software License (the "License"). You may not use # this file except in compliance with the License. A copy of the License is # located at: # # http://aws.amazon.com/asl/ # # or in the "license" file accompanying this file. This file is distributed # on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, express # or implied. See the License for the specific language governing # permissions and limitations under the License. import hashlib from datetime import datetime from awsglue.transforms import * from awsglue.context import GlueContext from pyspark.context import SparkContext import utils class Resource(object): def __init__(self, database, table_name, kind, catalog_id=None): self.database = database self.table_name = table_name self.catalog_id = catalog_id self.kind = kind class Source(Resource): def __init__(self, database, table_name, source_kind, catalog_id): Resource.__init__(self, database, table_name, "SOURCE", catalog_id) self.source_kind = source_kind class JDBCSource(Source): def __init__(self, database, table_name, catalog_id, source_prefix): Source.__init__(self, database, table_name, "JDBC", catalog_id) self.source_prefix = source_prefix class Target(Resource): def __init__(self, database, table_name, catalog_id, S3_location, target_prefix, output_format, job_name, job_run_id, table_config, temp_prefix): Resource.__init__(self, database, target_prefix + table_name, "TARGET", catalog_id) self.S3_location = S3_location self.target_prefix = target_prefix self.output_format = output_format self.job_name = job_name self.job_run_id = job_run_id self.table_config = table_config self.temp_prefix = temp_prefix # all prefixes already have a trailing '_' self.temp_table_name = "{}{}{}".format(temp_prefix, target_prefix, table_name) class Transform(object): def __init__(self, glue_client, source, target, glue_context, target_location): self.glue_client = glue_client self.source = source self.target = target self.table_exists = False self.glue_context = glue_context self.target_location = target_location self.source_schema = self.glue_client.get_table(CatalogId=self.source.catalog_id, DatabaseName=self.source.database, Name=self.source.table_name)['Table']['StorageDescriptor']['Columns'] def get_schema(self, partition_spec): return [{"Name": i['Name'], "Type": i['Type']} for i in self.source_schema if i['Name'] not in partition_spec] def get_mappings(self): return [(i['Name'], i['Name'], i['Type']) for i in self.source_schema] def _snapshot_transform(self): datasource0 = self.glue_context.create_dynamic_frame.from_catalog(database=self.source.database, catalog_id=self.source.catalog_id, table_name=self.source.table_name) applymapping1 = ApplyMapping.apply(frame=datasource0, mappings=self.get_mappings()) dropnullfields2 = DropNullFields.apply(frame=applymapping1) datasink3 = self.glue_context.write_dynamic_frame.from_catalog(frame=dropnullfields2, catalog_id=self.target.catalog_id, database=self.target.database, table_name=self.target.temp_table_name) def transform(self): self._snapshot_transform() class Driver(object): def __init__(self): args = utils.get_job_args(['JOB_NAME', 'JOB_RUN_ID', 'WORKFLOW_NAME', 'WORKFLOW_RUN_ID', 'region', 'source_table_prefix', 'glue_endpoint', 'catalog_id', 'target_s3_location', 'target_database', 'target_format', 'job_index', 'num_jobs'], ['target_table_prefix', 'creator_arn', 'version', 'encryption-type']) self.glue_endpoint = args['glue_endpoint'] self.region = args['region'] self.job_name = args['JOB_NAME'] self.job_run_id = args['JOB_RUN_ID'] self.workflow_name = args['WORKFLOW_NAME'] self.workflow_run_id = args['WORKFLOW_RUN_ID'] self.creator_arn = args['creator_arn'] self.glue_client = utils.build_glue_client(self.region, self.glue_endpoint) self.lf_client = utils.build_lakeformation_client(self.region, self.glue_endpoint) self.sc = SparkContext() self.glue_context = GlueContext(self.sc, minPartitions=1, targetPartitions=1) self.catalog_id = args['catalog_id'] self.target_database = args['target_database'] self.source_prefix = args['source_table_prefix'] self.target_prefix = args['target_table_prefix'] self.target_s3_location = args['target_s3_location'] self.output_format = args['target_format'] self.version = args['version'] if self.version and int(self.version) > 0: self.temp_prefix = "_temp_" else: self.temp_prefix = "temp_" self.tables = self.get_tables_config(int(args['job_index']), int(args['num_jobs'])) def table_exists(self, table_name): try: self.glue_client.get_table(CatalogId=self.catalog_id, DatabaseName=self.target_database, Name=table_name) return True except: return False def should_process_table(self, job_index, num_jobs): def h(table_config): catalog_table_name = table_config['catalog_table_name'] md5 = int(hashlib.md5(catalog_table_name).hexdigest(), 16) return (md5 % num_jobs) == job_index return h def get_storage_descriptor(self, format, schema, table_name): if format.lower() == "parquet": input_format = 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.parquet.MapredParquetInputFormat' output_format = 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.parquet.MapredParquetOutputFormat' serde_info = {'Parameters': {'serialization.format': '1'}, 'SerializationLibrary': 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.parquet.serde.ParquetHiveSerDe'} elif format.lower() == "csv": input_format = "org.apache.hadoop.mapred.TextInputFormat" output_format = "org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.HiveIgnoreKeyTextOutputFormat" serde_info = {'SerializationLibrary': 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.lazy.LazySimpleSerDe', 'Parameters': {'field.delim': ','}} elif format.lower() == "json": input_format = "" output_format = "" serde_info = {} else: raise Exception("Format should be CSV or Parquet, but got: {}".format(format)) return {'Columns': schema, 'InputFormat': input_format, 'OutputFormat': output_format, 'SerdeInfo': serde_info, 'Location': self.target_s3_location + table_name + "/"} def create_table(self, source, target, transform): #TODO: comment out JDBC partitioning #schema = transform.get_schema(source.partition_spec) schema = transform.source_schema table_input = {'Name': target.table_name, 'StorageDescriptor' : self.get_storage_descriptor(target.output_format, schema, target.table_name), 'Parameters': {'classification': target.output_format, 'SourceType': source.source_kind, 'SourceTableName': source.table_name[len(source.source_prefix):], 'CreatedByJob': target.job_name, 'CreatedByJobRun': target.job_run_id, 'TableVersion': "0"}, 'TableType': 'EXTERNAL_TABLE' } get_table_result = self.glue_client.get_table(CatalogId=source.catalog_id, DatabaseName=self.target_database, Name=source.table_name)['Table'] table_input['Parameters']['SourceConnection'] = get_table_result['Parameters']['connectionName'] if target.output_format.lower() == "csv": table_input['Parameters']['skip.header.line.count'] = "1" self.glue_client.create_table(CatalogId=target.catalog_id, DatabaseName=target.database, TableInput=table_input) table_input['Name'] = target.temp_table_name table_input['StorageDescriptor']['Location'] += "version_0/" self.glue_client.create_table(CatalogId=target.catalog_id, DatabaseName=target.database, TableInput=table_input) target.storage_descriptor = self.get_storage_descriptor(target.output_format, schema, source.table_name) def update_table(self, src, tgt): source = self.glue_client.get_table(CatalogId=src.catalog_id, DatabaseName=src.database, Name=src.table_name)['Table'] target = self.glue_client.get_table(CatalogId=tgt.catalog_id, DatabaseName=tgt.database, Name=tgt.table_name)['Table'] source_schema = source['StorageDescriptor']['Columns'] table_input = {key: target[key] for key in target if key not in ['CreatedBy', 'CreateTime', 'UpdateTime', 'DatabaseName']} table_input['StorageDescriptor']['Columns'] = source_schema #prev_version = "0" if ('Parameters' not in table_input or 'TableVersion' not in table_input['Parameters']) else table_input['Parameters']['TableVersion'] prev_version = table_input['Parameters']['TableVersion'] new_version = str(int(prev_version) + 1) table_input['Parameters']['TableVersion'] = new_version new_location = table_input['StorageDescriptor']['Location'][:-len("version_" + prev_version + "/")] table_input['StorageDescriptor']['Location'] = new_location + "version_" + new_version + "/" table_input['Name'] = tgt.temp_table_name print("[INFO] Trying to update: Source table: {}, TargetTable: {}".format(src.table_name, table_input['Name'])) self.glue_client.update_table(CatalogId=tgt.catalog_id, DatabaseName=tgt.database, TableInput=table_input) def hot_swap_tables(self, source, target, delta, end_time): temp = self.glue_client.get_table(CatalogId=target.catalog_id, DatabaseName=target.database, Name=target.temp_table_name)['Table'] tgt = self.glue_client.get_table(CatalogId=target.catalog_id, DatabaseName=target.database, Name=target.table_name)['Table'] table_input = {key: tgt[key] for key in tgt if key not in ['CreatedBy', 'CreateTime', 'UpdateTime', 'DatabaseName']} table_input['StorageDescriptor']['Columns'] = temp['StorageDescriptor']['Columns'] table_input['StorageDescriptor']['Location'] = temp['StorageDescriptor']['Location'] table_input['Parameters']['TableVersion'] = temp['Parameters']['TableVersion'] table_input['Parameters']['LastUpdatedByJob'] = target.job_name table_input['Parameters']['LastUpdatedByJobRun'] = target.job_run_id table_input['Parameters']['TransformTime'] = delta table_input['Parameters']['LastTransformCompletedOn'] = end_time self.glue_client.update_table(CatalogId=target.catalog_id, DatabaseName=target.database, TableInput=table_input) def update_table_job_info(self, source, target, delta, end_time): source = self.glue_client.get_table(CatalogId=target.catalog_id, DatabaseName=target.database, Name=source.table_name)['Table'] table_input = {key: source[key] for key in source if key not in ['CreatedBy', 'CreateTime', 'UpdateTime', 'DatabaseName']} table_input['Parameters']['LastUpdatedByJob'] = target.job_name table_input['Parameters']['LastUpdatedByJobRun'] = target.job_run_id table_input['Parameters']['TransformTime'] = delta table_input['Parameters']['LastTransformCompletedOn'] = end_time if 'TableType' not in table_input: table_input['TableType'] = 'EXTERNAL_TABLE' self.glue_client.update_table(CatalogId=target.catalog_id, DatabaseName=target.database, TableInput=table_input) def get_tables_config(self, job_index, num_jobs): table_list = [] next_token = '' while (True): get_tables_result = self.glue_client.get_tables(DatabaseName=self.target_database, CatalogId=self.catalog_id, Expression="^{}.*".format(self.source_prefix), NextToken=next_token) next_token = get_tables_result.get('NextToken') table_list.extend([t['Name'] for t in get_tables_result['TableList']]) if not next_token: break result = [{'catalog_table_name': i, "sourceType": "JDBC"} for i in table_list] selected_tables = filter(self.should_process_table(job_index, num_jobs), result) print("[INFO]: Will process {} tables: {}".format(len(selected_tables), [config['catalog_table_name'] for config in selected_tables])) return selected_tables def run_transform(self): for i in self.tables: if i.get("sourceType") == "JDBC": source = JDBCSource(self.target_database, i.get('catalog_table_name'), self.catalog_id, self.source_prefix) original_table_name = i.get('catalog_table_name')[len(source.source_prefix):] target = Target(self.target_database, original_table_name , self.catalog_id, self.target_s3_location, self.target_prefix, self.output_format, self.job_name, self.job_run_id, i, self.temp_prefix) transform = Transform(self.glue_client, source, target, self.glue_context, self.target_s3_location) print("[INFO] Source table name: {}, target table name: {}".format(source.table_name, target.table_name)) if not self.table_exists(target.table_name): print("[INFO] Target Table name: {} does not exist.".format(target.table_name)) self.create_table(source, target, transform) target_table_already_exists = False else: print("[INFO] Target Table name: {} exist.".format(target.table_name)) self.update_table(source, target) target_table_already_exists = True start_time = datetime.now() transform.transform() end_time = datetime.now() self.hot_swap_tables(source, target, str(end_time - start_time), str(end_time)) # Give permissions to the table if we are just creating it for the first time if not target_table_already_exists: utils.grant_all_permission_to_creator(self.lf_client, target.catalog_id, target.database, target.table_name, self.creator_arn) else: print("[INFO] Not setting up permissions for the creator on the ingested table") def main(): driver = Driver() driver.run_transform() if __name__ == "__main__": main()
簡単に内容を見ていきましょう。
main() 関数では Driver クラスの run_transform() を呼び出しています。
def main(): driver = Driver() driver.run_transform()
Driver クラスはコンストラクタでジョブ引数により初期化が行われます。
run_transform() でやっていることは単純で、大まかな流れとしては以下のようになっています。
# (1) source = JDBCSource(...) target = Target(...) transform = Transform(...) # (2) if not self.table_exists(target.table_name): self.create_table(source, target, transform) target_table_already_exists = False else: self.update_table(source, target) target_table_already_exists = True # (3) transform.transform() # (4) self.hot_swap_tables(source, target, ...) # (5) if not target_table_already_exists: utils.grant_all_permission_to_creator(...)
(1) でデータソースとターゲット、及び変換を行うクラスのインスタンスを取得
(2) ではデータカタログの定義を作成または更新(クローラにより収集したデータソースの情報からターゲットテーブルのメタ情報を作成) 新規作成時は version_0/ 、更新時は "version_" + new_version + "/" というロケーションが設定される(S3上のターゲットパスになる)。
(3) の変換処理で、PySpark によるETL処理
(4) では、書き込み後のデータカタログのスワップ(temp として作成したデータターゲットのカタログを正式化)
(5) で新しく作成されたテーブルにパーミッション設定
という流れになります。
ちなみに、並列ジョブでどのテーブルを処理するのかは、以下のようにテーブル名のハッシュ値から計算されます。
catalog_table_name = table_config['catalog_table_name'] md5 = int(hashlib.md5(catalog_table_name).hexdigest(), 16) return (md5 % num_jobs) == job_index
空いたジョブが処理対象を選択するのではなく、テーブル名によりどのジョブで処理するかが固定化されるため、レコード数により早く終るジョブとそうでないジョブが出てきます。
ETL 事後ジョブ
最後のジョブは、こちらの状態を変更しているだけです。
import utils FAILURE_STATE_TRANSITION_MAP = { 'DISCOVERING': 'DISCOVERY FAILED', 'IMPORTING': 'IMPORT FAILED', 'DISCOVERY FAILED': 'DISCOVERY FAILED', 'IMPORT FAILED': 'IMPORT FAILED' } def main(): args = utils.get_job_args([ 'WORKFLOW_NAME', 'WORKFLOW_RUN_ID', 'transition_state', 'glue_endpoint', 'region' ], []) workflow_name = args['WORKFLOW_NAME'] workflow_run_id = args['WORKFLOW_RUN_ID'] transition_state = args['transition_state'] glue_endpoint = args['glue_endpoint'] region = args['region'] client = utils.build_glue_client(region, glue_endpoint, True) state_to_set = transition_state run_properties = client.get_workflow_run_properties(Name=workflow_name, RunId=workflow_run_id)["RunProperties"] if transition_state == 'FAILED' and \ 'run_state' in run_properties and \ run_properties['run_state'] in FAILURE_STATE_TRANSITION_MAP: state_to_set = FAILURE_STATE_TRANSITION_MAP[run_properties['run_state']] if 'run_state' in run_properties: print("[INFO]: WORKFLOW {} CHANGING FROM STATE {} -> {}".format(workflow_name, run_properties['run_state'], transition_state)) run_properties['run_state'] = state_to_set client.put_workflow_run_properties(Name=workflow_name, RunId=workflow_run_id, RunProperties=run_properties) main()
今までみてきたものと同じですね。
まとめ
Lake Formation のブループリントで生成されるワークフローの Glue ジョブについて簡単に眺めてみました。
えぇ、ただそれだけです。