- Trie(prefix tree) とは
- 単純な Trie の実装
- Trie へのデータ登録処理
- Trie での検索処理
- Trie の動作
- Trie の改良
- Trie によるサジェスト
- 辞書の削除
- まとめ
Trie(prefix tree) とは
ある文字列が辞書に含まれるかどうかを高速に検索できるのが、Trie です。
Trie は retrieval が語源で「トゥリー」となりますが、ツリー構造(tree)と混同するため、try 「トライ」と呼ばれます。 別名 prefix tree とも言います。
スペルチェッカやオートコンプリートなどの大量の辞書データ中に目的の語が存在するかを調べる場合の実装として良く使われます。 長さ m の文字検索の計算量は O(m) となり、高速な検索処理が実現できます。
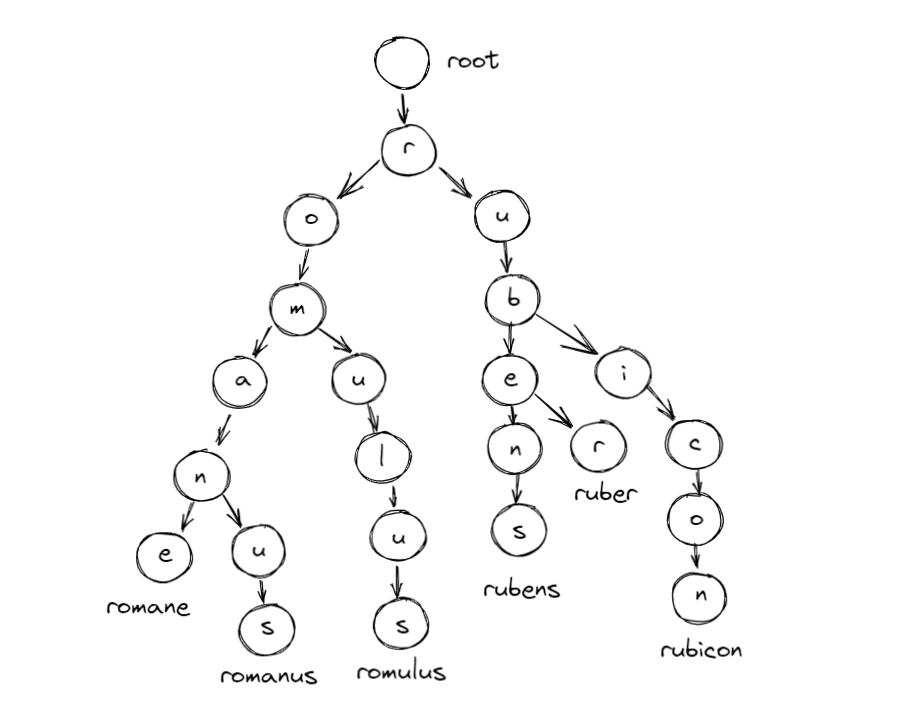
trie は以下のような木構造となり、木構造上のノードの位置とキーを対応させて格納します。
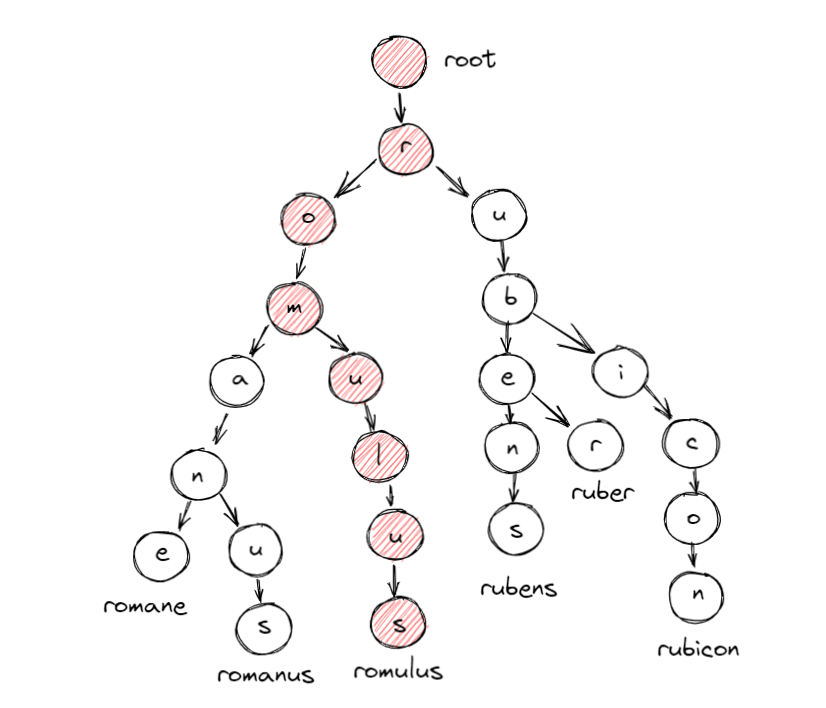
王政ローマ建国の初代王 romulus が辞書に含まれるかは以下のように文字数分のノードを辿ることで辞書との合致チェックができます。
ulus 部分をまとめて1つのノードとすることで、辿るノードを削減することもでき、その場合はさらに高速化が期待できます。
単純な Trie の実装
検索文字がアルファベットのみとした場合、子ノードへの参照は要素が26の配列を用意し、配列のインデックスでキー値を表現できます。
ノードを TrieNode とすれば、子ノードへの参照は TrieNode[26] children として表現し、children[ch - 'a'] とすることで、キーに応じたノードへマップできます。
TrieNode は以下のような実装になるでしょう。
public class TrieNode { private final TrieNode[] children; private boolean endOfWord; TrieNode() { children = new TrieNode[26]; } boolean contains(char ch) { return children[ch - 'a'] != null; } TrieNode get(char ch) { return children[ch -'a']; } void put(char ch, TrieNode node) { children[ch - 'a'] = node; } void setEndOfWord() { endOfWord = true; } boolean isEndOfWord() { return endOfWord; } }
endOfWord では、このノードで辞書としての単語が終了するかどうかをフラグとして管理します。abc abcd と辞書に登録があった場合、c のノードには endOfWord フラグを立てることで、単語境界を管理します。
この TrieNode を使い、Trie を以下のように定義できます。
public class Trie { private final TrieNode root; public Trie() { root = new TrieNode(); } public void insert(String word) { /* */ } public boolean search(String word) { /* */ } public boolean startsWith(String prefix) { /* */ } }
Trie へのデータ登録処理
辞書の値である word を Trie へ登録する処理は以下のようになります。
public class Trie { // ... public void put(String word) { TrieNode node = root; for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) { char ch = word.charAt(i); if (!node.contains(ch)) { node.put(ch, new TrieNode()); } node = node.get(ch); } node.setEndOfWord(); } }
root から辿り、キーが存在しなければ登録、存在すれば子を再帰的に辿ります。
Trie での検索処理
searchPrefix() というヘルパを用意します。検索する単語の前方から見ていき、Trie上に存在しなくなった場合は null、存在する場合はそのノードを返します。
public class Trie { // ... private TrieNode searchPrefix(String word) { TrieNode node = root; for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) { char ch = word.charAt(i); if (node.contains(ch)) { node = node.get(ch); } else { return null; } } return node; } }
完全一致を調べる search()、前方一致(最長)を調べる startsWith() は以下のように実装できます。
public class Trie { // ... public boolean search(String word) { TrieNode node = searchPrefix(word); return node != null && node.isEndOfWord(); } public boolean startsWith(String prefix) { return searchPrefix(prefix) != null; } }
Trie の動作
以下のデータを準備します。
Trie trie = new Trie(); trie.put("romane"); trie.put("romanus"); trie.put("romulus"); trie.put("rubens"); trie.put("ruber"); trie.put("rubicon");
完全一致を調べる search() は以下のように動作します。
trie.search("romane"); // -> true trie.search("romanus"); // -> true trie.search("roma"); // -> false trie.search("roman"); // -> false trie.search("apple"); // -> false trie.search("romules"); // -> false trie.search("rubicundus"); // -> false
前方一致(最長)を調べる startsWith() は以下のように動作します。
trie.startsWith("roma"); // -> true trie.startsWith("roman"); // -> true trie.startsWith("apple"); // -> false trie.startsWith("romules"); // -> false trie.startsWith("rubicundus"); // -> false
簡単でしたね。
Trie の改良
Trie の実装が簡単に実装できることは分かりましたが、通常はもう少し工夫を行います。
前述の例では、アルファベットだけの対応でしたが、任意文字を扱えるようにしましょう。
TrieNode[] children と配列で扱っていましたが、任意文字を考えた場合は巨大な配列が必要になってしまうため、マップに変えます。
キー絵文字なども考慮し codePoint で扱うことにしましょう。
TrieNode は以下のように変更するだけです。
public class TrieNode { private final Map<Integer, TrieNode> children; private boolean endOfWord; TrieNode() { children = new HashMap<>(); } TrieNode createIfAbsent(Integer key) { return children.computeIfAbsent(key, k -> new TrieNode()); } boolean contains(int codePoint) { return children.containsKey(codePoint); } TrieNode get(int codePoint) { return children.get(codePoint); } void put(int codePoint, TrieNode node) { children.put(codePoint, node); } // ... }
Trie の変更も軽微で、codePoint を扱うようにした程度です。
public class Trie { public void put(String word) { TrieNode node = root; for (int i = 0; i < word.length();) { int cp = word.codePointAt(i); node = node.createIfAbsent(cp); i += Character.charCount(cp); } node.setEndOfWord(); } // ... private TrieNode searchPrefix(String word) { TrieNode node = root; for (int i = 0; i < word.length();) { int cp = word.codePointAt(i); if (node.contains(cp)) { node = node.get(cp); } else { return null; } i += Character.charCount(cp); } return node; } }
これで、以下のような検索もできるようになります。
trie.search("😊❤");
Trie によるサジェスト
TrieNode に以下を追加し、
public class TrieNode { List<String> childKeys() { return children.keySet().stream().map(Character::toString).toList(); } }
入力内容の次単語をサジェストとして得るようにすることもできます。
private List<String> suggestion(String word) { TrieNode node = root; for (int i = 0; i < word.length();) { int cp = word.codePointAt(i); if (node.contains(cp)) { node = node.get(cp); } else { break; } i += Character.charCount(cp); } return node.childKeys(); }
ここでは、次の1単語のみのサジェストですが、続く複数語のサジェストも容易でしょう。
辞書の削除
最後に Trie に登録した単語の削除も見ておきましょう。
削除時には、子ノードから親ノードを参照できると便利なので、TrieNode に親への参照を保持するように変更します。
public class TrieNode { private final TrieNode parent; // ... TrieNode(TrieNode parent) { this.parent = parent; this.children = new HashMap<>(); } TrieNode createIfAbsent(Integer key) { return children.computeIfAbsent(key, k -> new TrieNode(this)); } // ... }
Trie のルートノードの親には null を設定します。
public class Trie { private final TrieNode root; public Trie() { root = new TrieNode(null); } // ... }
これで子ノードから親ノードへのリンクが追加できたので、削除処理を実装します。
Trie に削除用の remove() メソッドを追加します。
public class Trie { // ... public void remove(String word) { TrieNode node = searchPrefix(word); if (node == null || !node.isEndOfWord()) { return; } node.setEndOfWord(false); node.removeIfEmpty(); } }
TrieNode に削除用の removeIfEmpty() を追加し、親へと再帰的に削除処理を行います。
public class TrieNode { // ... void removeIfEmpty() { if (parent == null) { return; } if (children.isEmpty()) { parent.children.remove(key()); parent.removeIfEmpty(); } } private Integer key() { if (parent == null) { return null; } return parent.children.entrySet().stream() .filter(e -> e.getValue() == this) .findFirst() .map(Map.Entry::getKey) .orElse(null); } }
以下のようになります。
Trie trie = new Trie(); trie.put("romane"); trie.put("romanus"); trie.put("romulus"); trie.search("romane"); // -> true trie.search("romanus"); // -> true trie.search("romulus"); // -> true trie.remove("romanus"); trie.remove("romulus"); trie.search("romane"); // -> true trie.search("romanus"); // -> false trie.search("romulus"); // -> false
まとめ
スペルチェッカやサジェスチョンで利用されるデータ構造、Trie について説明しました。 Patricia tree や binary trie など色々な Trie の派生もありますが、Trie 自体は実装もシンプルで使いやすいため、何かの折に参考になればと思います。
今回の実装例の全体は以下に張り付けておきます。
import java.util.*; public class TrieNode { private final TrieNode parent; private final Map<Integer, TrieNode> children; private boolean endOfWord; TrieNode(TrieNode parent) { this.parent = parent; this.children = new HashMap<>(); } TrieNode createIfAbsent(Integer key) { return children.computeIfAbsent(key, k -> new TrieNode(this)); } boolean contains(int codePoint) { return children.containsKey(codePoint); } TrieNode get(int codePoint) { return children.get(codePoint); } void put(int codePoint, TrieNode node) { children.put(codePoint, node); } void removeIfEmpty() { if (parent == null) { return; } if (children.isEmpty()) { parent.children.remove(key()); parent.removeIfEmpty(); } } private Integer key() { if (parent == null) { return null; } return parent.children.entrySet().stream() .filter(e -> e.getValue() == this) .findFirst() .map(Map.Entry::getKey) .orElse(null); } List<String> childKeys() { return children.keySet().stream().map(Character::toString).toList(); } void setEndOfWord() { endOfWord = true; } void setEndOfWord(boolean endOfWord) { this.endOfWord = endOfWord; } boolean isEndOfWord() { return endOfWord; } }
import java.util.List; public class Trie { private final TrieNode root; public Trie() { root = new TrieNode(null); } public void put(String word) { TrieNode node = root; for (int i = 0; i < word.length();) { int cp = word.codePointAt(i); node = node.createIfAbsent(cp); i += Character.charCount(cp); } node.setEndOfWord(); } public void remove(String word) { TrieNode node = searchPrefix(word); if (node == null || !node.isEndOfWord()) { return; } node.setEndOfWord(false); node.removeIfEmpty(); } public boolean search(String word) { TrieNode node = searchPrefix(word); return node != null && node.isEndOfWord(); } public boolean startsWith(String prefix) { return searchPrefix(prefix) != null; } private TrieNode searchPrefix(String word) { TrieNode node = root; for (int i = 0; i < word.length();) { int cp = word.codePointAt(i); if (node.contains(cp)) { node = node.get(cp); } else { return null; } i += Character.charCount(cp); } return node; } public List<String> suggestion(String word) { TrieNode node = root; for (int i = 0; i < word.length();) { int cp = word.codePointAt(i); if (node.contains(cp)) { node = node.get(cp); } else { break; } i += Character.charCount(cp); } return node.childKeys(); } }