はじめに
とあるシステムで Chrome では動くけど、Firefox だと動かないという障害がありました。
JavaEE の Flash スコープを使った箇所で問題が発生しており、追っていくとブラウザ間で異なる Cookie の扱い方が原因でした。
Chrome と Firefox で異なる Cookie の扱いをメモしておきます。
Cookie 検証用コード
以下のような簡単な検証用のコードを用意しました。
@Path("/hello") @Produces(MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN) public class ExampleResource { @GET @Produces(MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN) @Path("/cookie/1") public String cookie1( @PathParam("id") Long id, @Context HttpServletRequest request, @Context HttpServletResponse response) { Cookie cookie = new Cookie("cookie", "1"); cookie.setPath("/hello/cookie"); response.addCookie(cookie); return "ok"; } @GET @Produces(MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN) @Path("/cookie/2") public String cookie2( @PathParam("id") Long id, @Context HttpServletRequest request, @Context HttpServletResponse response) { Cookie cookie = new Cookie("cookie", "2"); cookie.setPath("/hello/cookie/"); response.addCookie(cookie); return "ok"; } @GET @Path("/cookie") public String cookie(@Context HttpServletRequest request) { return Arrays.toString(Arrays.stream(request.getCookies()) .map(c -> String.join(",", c.getName(), c.getValue())).toArray()); } }
/hello/cookie/1 で、/hello/cookie というパスで Cookie を設定します。
/hello/cookie/2 で、/hello/cookie/ というパスで Cookie を設定します。
違いは Cookie のパスが / で終わるか終わらないかです。
Chrome による Cookie 送信
/hello/cookie/1 と /hello/cookie/2 にアクセスした後は以下のように Cookie がセットされます。
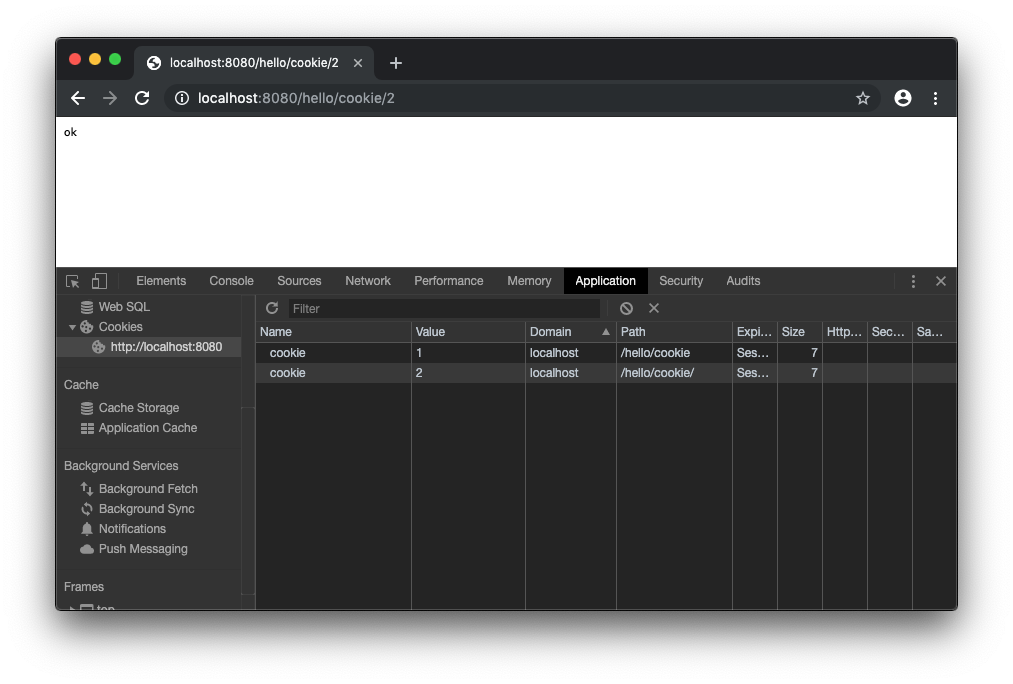
/hello/cookie でリクエストしてみます。
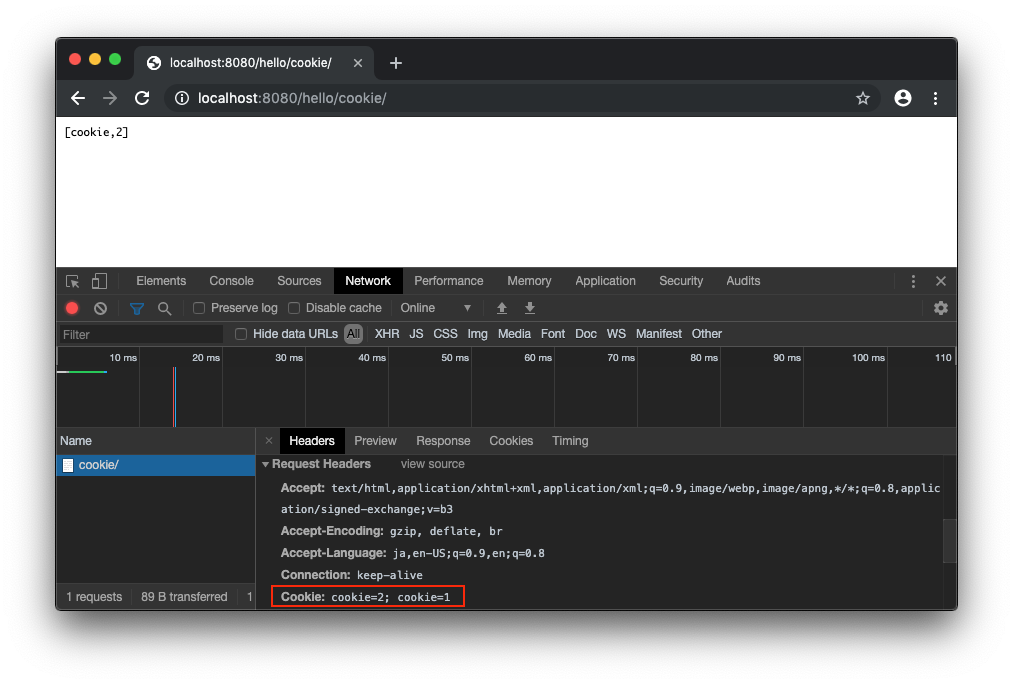
cookie=1 が送信されます。
/hello/cookie/ でリクエストしてみます。
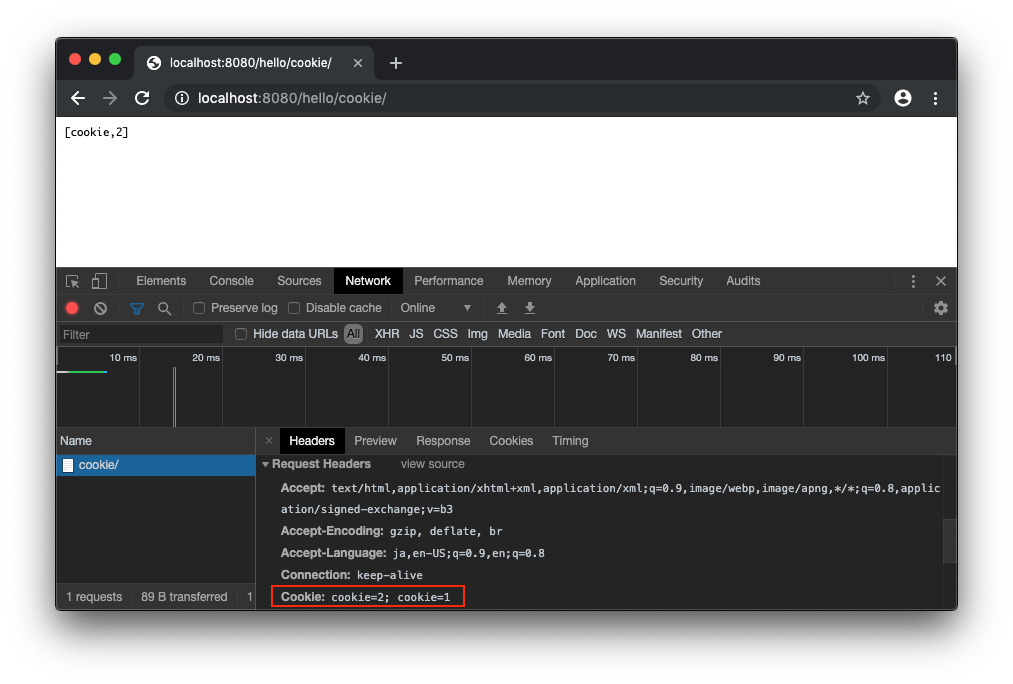
cookie=2 と cookie=1 が送信されていることがわかります。
HttpServletRequestで受けた場合は cookie=2 だけが取得できます。
Firefox による Cookie 送信
では、Firefox の場合ではどうでしょうか?
/hello/cookie/1 と /hello/cookie/2 にアクセスした後は以下のように Cookie がセットされます。
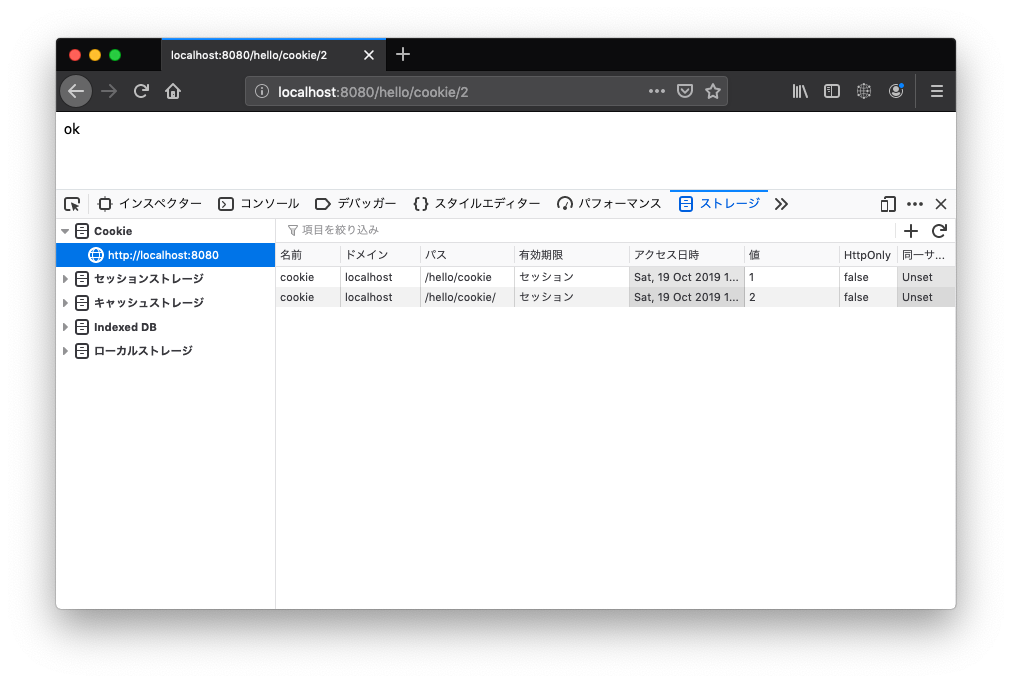
/hello/cookie でリクエストしてみます。
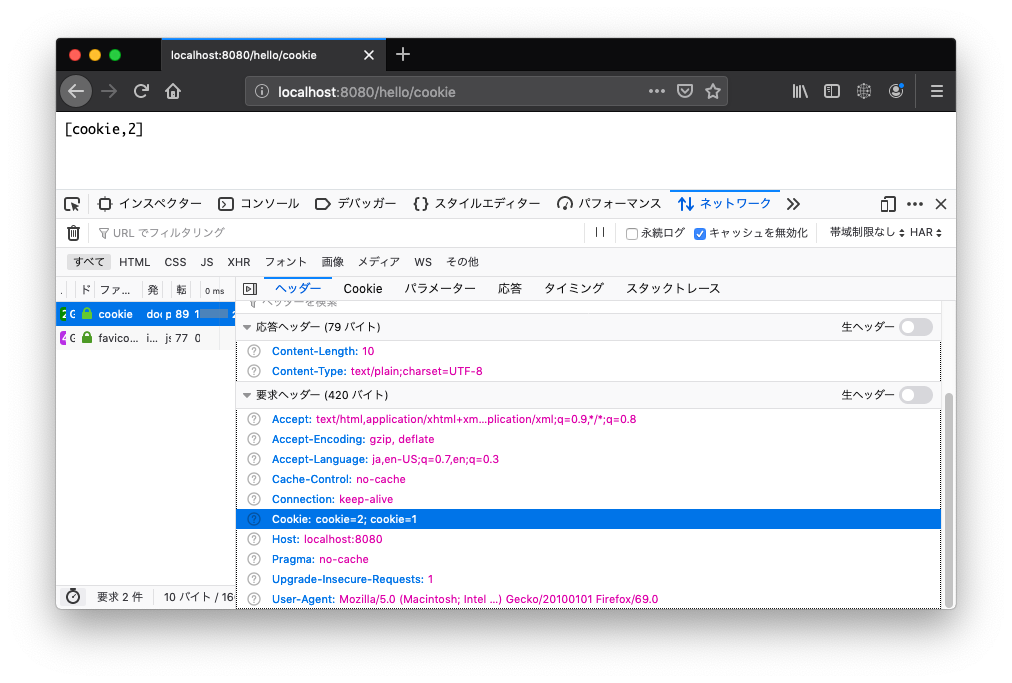
Chrome では cookie=1 のみでしたが、Firefox では cookie=2 と cookie=1 が送信されました。
/hello/cookie/ でリクエストしてみます。
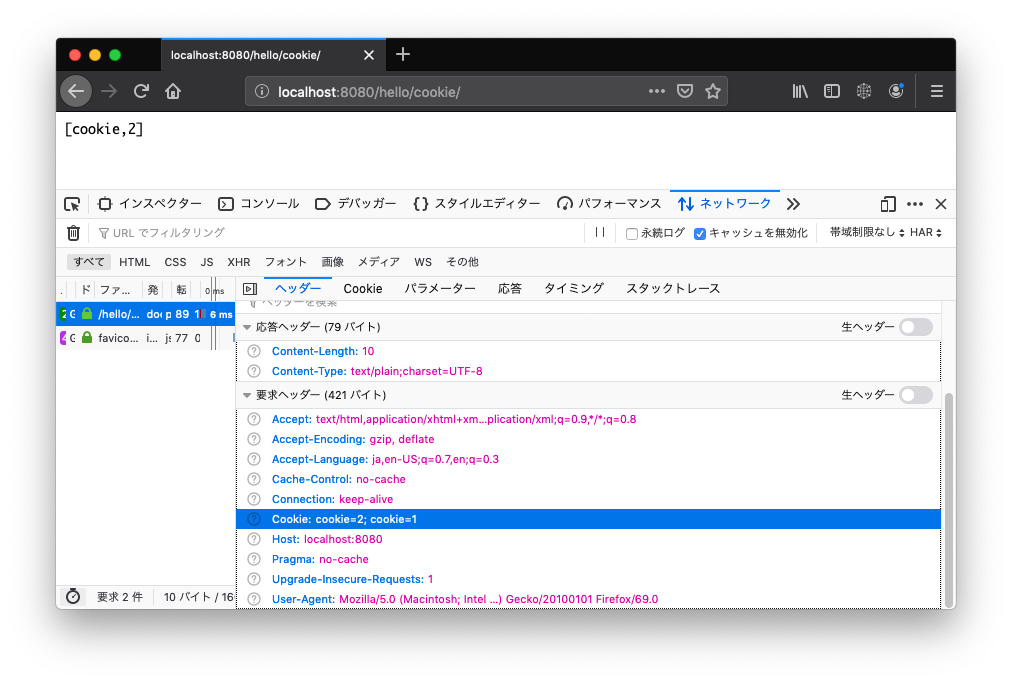
こちらも同様に cookie=2 と cookie=1 が送信されました。
いずれの場合もHttpServletRequestで受けた場合は cookie=2 だけが取得されます。
RFC 6265 での定義
RFC 6265 では以下のように定義されています。
5.1.4. Paths and Path-Match
...
A request-path path-matches a given cookie-path if at least one of the following conditions holds:
o The cookie-path and the request-path are identical.
o The cookie-path is a prefix of the request-path, and the last character of the cookie-path is %x2F ("/").
o The cookie-path is a prefix of the request-path, and the first character of the request-path that is not included in the cookie- path is a %x2F ("/") character.
送信するかどうかは、以下の条件のどれかを満たせば送信するとなっています。
- cookie-path と request-path が同一
- cookie-path が request-path に前方一致、かつ cookie-path の最後の文字が
/ - cookie-path が request-path に前方一致、かつ (cookie-pathに含まれない) request-path の最初の文字が
/
今回のケースでは、cookie-path が /hello/cookie/ であり、request-path が /hello/cookie となり、cookie-path が request-path に前方一致しないので、Chrome は RFC 6265 に準拠しているようです。
Firefox は cookie-path として末尾の / を無視するようになっているようです。
まとめ
- Chrome では、cookie-path が
/hello/cookie/で request-path が/hello/cookieの場合 Cookie が送信されない - Firefoxでは、cookie-path が
/hello/cookie/で request-path が/hello/cookieの場合 Cookie が送信される
ちなみに、今回の検証ではバックエンドに Undertow を利用しており、Cookie の処理は以下のようになっています。
private static int createCookie(final String name, final String value, int maxCookies, int cookieCount, final Map<String, String> cookies, final Map<String, String> additional) { if (!name.isEmpty() && name.charAt(0) == '$') { if(additional.containsKey(name)) { return cookieCount; } additional.put(name, value); return cookieCount; } else { if (cookieCount == maxCookies) { throw UndertowMessages.MESSAGES.tooManyCookies(maxCookies); } if(cookies.containsKey(name)) { // (1) return cookieCount; } cookies.put(name, value); return ++cookieCount; } }
(1) の箇所で、最初にパースしたものが優先されるため、最初のものが有効になります。
他のサーブレット実装では異なる(後勝ち)場合があるかもしれません。

- 作者: 上野宣
- 出版社/メーカー: 翔泳社
- 発売日: 2013/08/09
- メディア: Kindle版
- この商品を含むブログ (7件) を見る

Real World HTTP ―歴史とコードに学ぶインターネットとウェブ技術
- 作者: 渋川よしき
- 出版社/メーカー: オライリージャパン
- 発売日: 2017/06/14
- メディア: 単行本(ソフトカバー)
- この商品を含むブログ (4件) を見る